This is about matter vs. antimatter.
Everyday items like lemon are creating antimatter.
So if you want to know what matter and antimatter are and how they differ, then you’re in the right place.
Let’s get started!
#1 What Is the Difference Between Matter and Antimatter?
In the beginning, the big bang burst forth, creating a universe made of matter and antimatter.
Matter, of course, makes up everything we know and see in the universe.
Whereas antimatter is nearly identical to its matter counterpart but carries the opposite spin and charge.
When the two counterparts interact, they instantly annihilate one another, leaving behind only energy.
Now, equal proportions of matter and antimatter should have been created in the big bang.

So, theoretically, all matter should have been destroyed in the early universe, and we should not exist.
Yet, something happened to allow the matter to win out, allowing everything we know to come into existence.
#2 How Is Antimatter Created?
Did you know that everyday items in your home are creating antimatter?
Foods containing potassium-40, a naturally occurring radioactive isotope, spit out various antiparticles.
For instance, bananas generate one positron (counterpart of the electron) every 75 minutes.
Carrots, red meat, beer, lima beans, and several other common foods also produce antimatter particles.
However, none of these food items are exposing us to lethal doses of radioactivity.
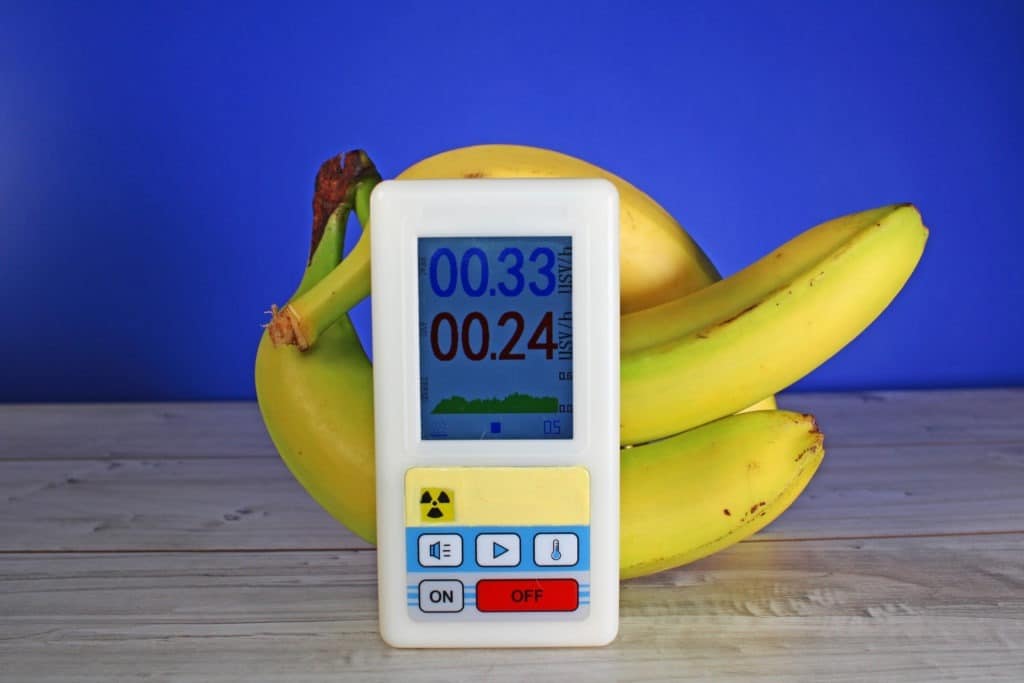

Actually, you would need to eat over 800 bananas in a single day to even reach mild doses of radiation.
#3 You Are Creating Antimatter
Yes, your own human body is producing and emitting positron antimatter particles.
Similar to bananas, your body contains potassium-40, along with trace amounts of carbon-14, uranium, and more.
Therefore, as these natural isotopes decay, you emit positron particles every so often.
Now, positrons have a positive electric charge.
So, upon meeting their electron counterparts with a negative charge, the two instantaneously destroy each other.
Therefore, the antimatter particles your body creates only last for a mere moment.
#4 Can Humans Make Antimatter?
Like most things in life, humans have tried and succeeded in generating manmade antimatter.
Laboratories and colliders from all over the world have slowly produced small but measurable amounts of antiparticles.

Matter and antimatter interactions have the potential to generate staggering amounts of energy.
In fact, a single gram of antimatter can yield the equivalent of an atomic bomb.
So, should we be concerned with malevolent people learning the art of antimatter creation?
Not currently, no.
Even world-renown labs, like CERN and Fermilabs, have generated a combined 15 nanograms of antimatter.
Ultimately, this adds up to 0.0000015% of a single gram.
In other words, the energy produced by all manmade antimatter would not even boil a pot of water.

Producing antimatter in a lab simply costs too much, takes too long to create, and is too difficult to store.
Actually, producing a full gram of antimatter would cost millions of billions of dollars and require hundreds of thousands of hours.
#5 Where Did All the Antimatter Go?
Equal amounts of matter and antimatter should have been created by our universe. Therefore, matter, as we know it, could not have existed.
Humans could not exist.
However, normal matter somehow won and exists in drastically larger quantities throughout the universe than antimatter.
Yet, nobody currently knows what happened to allow the matter to win.
Currently, this is one of physics’ hottest topics and largest searches.
Actually, some modern theories believe the missing antimatter is still out in space somewhere.

The International Space Station even has highly advanced equipment attached to it to help detect antiparticles traveling in cosmic rays.
Yet, we currently have little evidence of antimatter existing in bulk anywhere in the universe.
Unfortunately, the search continues, and the cause of matter and antimatter asymmetry remains a mystery.